MEMORY
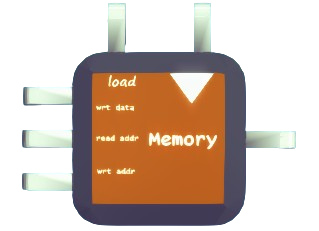
Similar to REG, but can store many signal with corresponding address.
Input Ports
There are three input ports:
i1: with the type ofany, the signal that you want to store in memory.i2: with the type of float, the memory address, from where you want to read the data (output).i3: with the type of float, the memory address that you want the signal to be written into.
Control Ports
Same with REG
There are two control ports, c1 and c2
c1is the clock signal that will trigger the storage operation.booltypec2is the load signal that controls whether the unit should load data fromi1.booltype.
Output Ports
Same with REG
There is one output port o1, with type of any.
Function
Once the storage operation is triggered, MEMORY will first see the value of c1(load). If true, REG will read the signal of i1 and i3, corresponding to data and store address. Then, MEMORY will change the value in storage address to that data.
If false, MEMORY will not do storage operation.
Once i2, the read address is changed, MEMORY will update o1 with the stored data with corresponding address immediately.
If a address has not been written with any data, the read operation's output will be null.
If i2 or i3 is null, they will be interpreted as 0(float) and the memory will behave exactly the same as REG