
一、 自觉遵守团队活动纪律,尊敬师长、友爱同学,讲文明、懂礼貌,有诚信。

一、 自觉遵守团队活动纪律,尊敬师长、友爱同学,讲文明、懂礼貌,有诚信。
process:
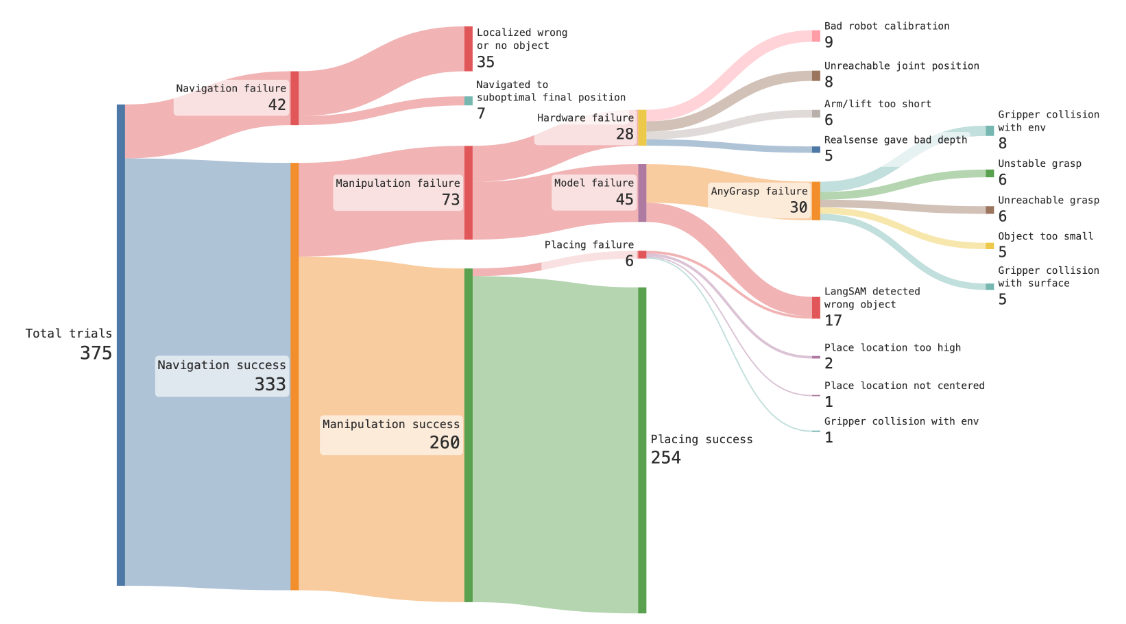
KAF-Net: Part-level Kinematic Relation Graph Generation For Robot Manipulation
| backbone | In. Aug | class balance | $mAp_{50}$ | $R@10/20/40$ | $mR@10/20/40$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SwinT | MCM | yes | 24.2 | 33.4/53.8/73.9 | 25.1/52.9/69.2 |
| no | 23.4 | 43.5/62.3/78.7 | 26.9/55.3/67.9 | ||
| Single | yes | 23.5 | 32.3/51.6/69.2 | 34.4/52.9/65.4 | |
| no | 24.2 | 32.7/51.4/68.6 | 25.2/53.5/66.3 | ||
| ResDCN | MCM | yes | 23.1 | 32.8/52.8/70.1 | 24.8/52.8/67.7 |
| no | 23.4 | 36.9/52.5/69.9 | 23.9/47.8/62.4 | ||
| Single | yes | 20.5 | 39.9/54.3/69.3 | 37.7/51.2/65.1 | |
| no | 22.3 | 33.8/52.4/69.4 | 35.7/55.6/66.7 | ||
| On Swin Transformer with class balance: |
| Image-Mask Branch | $mAp_{50}$ | $mR@10/20/40$ |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | ||
| No |
| VLM | VI | VR | unVR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | |||
| Pixtral 12B |
process:
在大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的问答和内容生成领域,检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)已成为一项基础技术。然而,传统的 RAG 依赖于向量相似度搜索,如同在图书馆中寻找内容相似的书籍,却常常忽略了书籍之间、作者之间以及知识点之间错综复杂的关系。为了突破这一局限,Graph RAG 应运而生,它通过引入“知识图谱”,为 RAG 系统装上了能够理解和导航数据关系的“智慧大脑”,实现了从“相关性检索”到“关联性推理”的重大飞跃。
标准 RAG 的工作流程通常是:
将大量文档切分成独立的文本块(chunks)。
将这些文本块向量化后存入向量数据库。
当用户提问时,将问题向量化并在数据库中进行相似度搜索,找出最相关的几个文本块。
将这些文本块作为上下文(Context)连同问题一起提供给 LLM,生成最终答案。
这种方法的缺陷在于,它处理的是孤立的信息片段。如果一个答案需要整合来自多个不同但相互关联的文档中的信息,标准 RAG 就可能力不从心。
Graph RAG 则彻底改变了数据的组织和检索方式:
构建知识图谱: 它不再仅仅是切分文档,而是利用 LLM 从非结构化文本中提取出关键的实体(Entities)和它们之间的关系(Relationships)。例如,从“埃隆·马斯克是特斯拉的CEO,该公司总部位于美国”这句话中,可以提取出实体“埃隆·G马斯克”、“特斯拉”、“CEO”、“美国”,以及关系“(马斯克)-是-(CEO)-属于-(特斯拉)”和“(特斯拉)-总部位于-(美国)”。
图谱化存储: 这些实体作为“节点(Nodes)”,关系作为“边(Edges)”,共同构建成一个庞大而精细的知识网络,并存储在专门的图数据库中。
基于关系的检索: 当用户提问时,Graph RAG 不仅进行语义搜索,更重要的是在图谱上进行遍历和路径查找。它能识别问题中的核心实体,然后在图谱中探索这些实体的邻近节点和多层关系,从而收集到一个结构化、高度关联且富有深度的上下文。
生成精准答案: 最后,将这个包含丰富实体和关系信息的子图(sub-graph)作为上下文提供给 LLM,使其能够基于清晰的逻辑链条进行推理,生成更精准、更具解释性的答案。
简单来说,标准 RAG 问的是“哪些文档与我的问题最像?”,而 Graph RAG 问的是“与我问题相关的实体有哪些?它们之间存在什么样的联系?这些联系如何共同解答我的问题?”
Graph RAG 的实现依赖于一个强大的技术栈,它融合了自然语言处理、图技术和大型模型。
大型语言模型 (LLMs): 在 Graph RAG 中扮演双重角色。
知识提取器: 在构建图谱阶段,使用 LLM 强大的自然语言理解能力,从海量非结构化或半结构化文本中自动识别实体和关系,极大地降低了知识图谱的构建门槛。
推理与生成器: 在查询阶段,LLM 负责理解从图谱中检索到的结构化上下文,并基于这些关系进行推理,最终生成流畅、准确的自然语言答案。
知识图谱 (Knowledge Graphs): 这是 Graph RAG 的核心。它以图的形式组织信息,完美地契合了真实世界中知识相互关联的特性,使得复杂的“多跳问题”(需要跨越多个信息点才能回答的问题)得以解决。
图数据库 (Graph Databases): 专为存储和查询知识图谱而设计的数据库,如 Neo4j, NebulaGraph, Amazon Neptune 等。与传统关系型数据库相比,图数据库能以极高的效率执行关系遍历和路径查找操作,这对于实时响应 Graph RAG 的复杂查询至关重要。
图算法与图机器学习:
社区发现算法 (e.g., Leiden): 在构建图谱后,可以对节点进行聚类,形成不同的“社区”或“主题域”。这使得 Graph RAG 可以实现“全局搜索”,先定位到最相关的社区,再进行细粒度检索。
图嵌入 (Graph Embeddings): 将图中的节点和关系也表示为向量,使得图结构信息可以和文本语义信息在同一个向量空间中进行融合与检索。
Graph RAG 的优势在于处理需要深度推理、上下文理解和关系挖掘的复杂场景,因此在以下领域展现出巨大潜力:
金融风控与合规: 在反欺诈场景中,Graph RAG 可以轻松识别出看似无关的交易、账户和个人之间隐藏的关联,揭示复杂的欺诈网络。在合规审查中,它可以将法规条款、公司行为和交易数据连接起来,提供可追溯、可解释的合规判断。
生物医学与药物研发: 生物医学领域充满了复杂的相互作用,如基因、蛋白质、疾病和药物之间的关系。Graph RAG 能够整合海量论文、临床试验数据和基因数据库,帮助研究人员发现新的药物靶点、预测药物副作用,或为特定患者提供个性化的治疗方案建议。
供应链管理: 现代供应链是一个复杂的全球网络。Graph RAG 可以整合供应商、物流、库存、市场需求和地缘政治风险等数据,当出现“某国港口关闭”等事件时,能迅速分析出受影响的上下游企业和产品,并推荐替代方案。
企业智能知识管理: 大型企业内部知识分散在不同部门的文档、报告和数据库中。Graph RAG 可以将这些知识整合成一个统一的、相互关联的企业知识图谱,让员工能以自然语言提问,获得跨部门、高精度的答案,例如“去年哪个产品的研发项目同时涉及了上海和硅谷的团队,并且项目负责人是谁?”
个人化推荐系统: 通过构建用户、产品、偏好和行为之间的关系图谱,Graph RAG 能够提供超越“购买此商品的人也购买了…”的简单推荐,实现更深层次的、基于兴趣和逻辑关联的个性化内容或产品推荐。
What is LangChain
What is LangGraph
在人工智能应用的浪潮中,大型语言模型(LLM)无疑是当前最耀眼的明星。然而,要将其强大的能力转化为实际、可靠且功能丰富的应用程序,开发者需要一套强而有力的框架。LangChain 和 LangGraph 正是为此而生的两大核心工具,它们极大地简化了 LLM 应用的开发流程,并为构建复杂的智能代理(Agent)提供了无限可能。
核心概念:
LangChain 是一个开源的应用程序开发框架,其核心理念在于“链(Chain)”的概念。它旨在将大型语言模型与外部资源(如数据库、API、文件等)以及其他计算逻辑无缝地“链接”起来。通过模块化的组件,开发者可以轻松地构建、组合和扩展 LLM 应用,从而实现超越简单文本生成的功能。
LangChain 的主要构成部分包括:
模型(Models): 整合了各类大型语言模型和嵌入模型的标准接口,开发者可以轻松切换和使用不同的模型。
提示(Prompts): 提供强大的提示模板管理功能,让开发者能够动态地生成和优化给予模型的指令。
索引(Indexes): 用于结构化和检索外部数据,是实现如“检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)”等应用的关键,让模型能够基于特定知识库回答问题。
链(Chains): 这是 LangChain 的核心,用于将多个组件(包括其他链)按顺序组合起来,形成一个完整的应用逻辑。
代理(Agents): 赋予 LLM 推理和行动的能力。代理程序可以使用一系列工具(Tools),并根据用户输入自主决定调用哪个工具来完成任务。
记忆(Memory): 让应用程序能够记住先前的对话内容,从而进行有上下文的、连贯的交流。
应用样例:
LangChain 的应用极为广泛,几乎涵盖了所有需要利用 LLM 进行自然语言处理的场景:
智能问答机器人: 结合企业内部文件或特定领域的知识库,打造能够精准回答专业问题的问答系统。例如,一个能够读取公司所有技术文档,并回答工程师技术问题的聊天机器人。
文件分析与摘要: 快速读取长篇报告、法律文件或学术论文,并生成简洁的摘要或提取关键信息。
数据分析与洞察: 通过自然语言查询,与结构化(如 SQL 数据库)或非结构化数据进行互动,生成分析报告和可视化图表。
自动化代码生成与解释: 根据需求描述自动生成代码片段,或对现有代码进行解释和除错。
个性化内容推荐: 根据用户的历史行为和偏好,生成个性化的新闻摘要、产品推荐或旅行计划。
核心概念:
随着应用需求的日益复杂,单纯的线性“链”式结构有时会显得力不从心。特别是在需要处理循环、条件分支和多个智能代理协同工作的场景下,LangGraph 应运而生。
LangGraph 是 LangChain 生态系中的一个扩展,它将 LLM 应用的流程从线性的“链”提升到了更灵活、更强大的“图(Graph)”的层次。在 LangGraph 中,应用的执行流程被定义为一个有向图,其中:
节点(Nodes): 代表工作流程中的一个步骤,可以是一个 LLM 的调用、一个工具的执行或一段自定义的 Python 代码。
边(Edges): 连接不同的节点,定义了信息在图中的流动方向。特别是“条件边(Conditional Edges)”,可以根据节点的输出结果,动态地决定下一步要跳转到哪个节点。
状态(State): 这是 LangGraph 的一个核心概念,它是一个在整个图形执行过程中持续存在的对象,用于存储和传递信息。每个节点都可以读取和更新这个共享的状态,从而实现了比线性链更复杂的记忆和上下文管理。
与 LangChain 的主要区别:
| 特性 | LangChain | LangGraph |
|---|---|---|
| 核心结构 | 线性、顺序执行的“链” | 灵活、可循环的“图” |
| 适用场景 | 简单到中等复杂度的顺序性任务 | 需要条件逻辑、循环和状态管理的复杂任务 |
| 流程控制 | 预先定义好的固定流程 | 动态、可根据执行结果改变的流程 |
| 复杂性 | 学习曲线相对平缓,易于上手 | 提供了更高的自由度和控制力,学习曲线稍陡 |
| 错误处理 | 需要在链的逻辑中自行定义重试机制 | 可以将错误处理设计为图中的一个独立节点 |
| 代表应用 | 问答系统、文件摘要、简单的工具调用 | 多代理协作、可自主修正的智能代理、人机协作流程 |
应用样例:
LangGraph 特别擅长于构建需要更强控制力和灵活性的高级应用:
多代理协同工作(Multi-agent Collaboration): 构建一个研究团队,其中一个代理负责上网搜索资料,另一个代理负责分析和整合资料,最后一个代理负责撰写报告。LangGraph 可以清晰地定义它们之间的协作流程、信息传递和审核机制。
具有自我修正能力的代理: 当一个代理执行的工具出错或结果不理想时,可以通过条件边将流程导向一个“反思与修正”的节点,让代理重新评估策略并尝试新的方法,形成一个不断试错和优化的循环。
人机协作(Human-in-the-loop): 在关键决策点,可以设计一个节点来暂停流程,并请求人类用户的输入或批准。例如,在一个自动下单的代理中,最终下单前需要由人类确认订单细节。
互动式故事生成: 根据用户的选择,故事的情节可以走向完全不同的分支,甚至可以回到之前的某个情节点,产生高度互动和非线性的叙事体验。
| 特性 | LangChain (Chains) | LangGraph |
|---|---|---|
| 结构 | **线性 (Linear)**:一步接一步,像流水线。 | **图形化 (Graphical)**:支持分支、合并和循环,像流程图。 |
| 控制流 | 预定义:流程在开始前就已固定。 | 动态:流程可以根据节点的输出实时改变。 |
| 核心场景 | 工具链/RAG:快速构建顺序性任务,如文档问答、API 调用。 | **智能代理 (Agents)**:构建需要决策、重试、多代理协作的复杂系统。 |
| 状态管理 | 简单:通常只在链的内部传递,难以实现全局、持久的状态。 | 核心特性:拥有一个明确的、贯穿始终的 State 对象,方便管理复杂上下文。 |
| 举例 | “读取 PDF -> 总结内容 -> 发送邮件” | “搜索信息 -> LLM 判断信息是否足够 -> 如果不足,重新搜索 -> 如果足够,撰写报告” |
LangChain 和 LangGraph 正处于高速发展和迭代的阶段,整个生态系也日益成熟和完善。
LangChain 的发展:
架构模块化: LangChain 逐渐将其核心功能拆分为 langchain-core 和 langchain-community 等多个包。langchain-core 提供了稳定和核心的抽象接口,而 langchain-community 则包含了大量的第三方集成,这样的架构使得核心框架更加稳定,同时也方便社区贡献和维护。
LangChain 表达式语言(LCEL): 这是 LangChain 近期最重要的更新之一。LCEL 提供了一种声明式的方式来组合链,使得代码更为简洁、直观,并且原生支持批量处理、并行执行、流式输出等高级功能。
LangSmith 的成熟: LangSmith 是一个用于监控、调试和评估 LLM 应用的平台。它提供了对应用执行过程的“X光”般的洞察力,让开发者可以清晰地看到每一步的输入、输出、延迟和令牌消耗,极大地提升了开发和维护效率。
LangServe 的推出: 为了方便将开发好的链或代理部署为生产级的 API,LangChain 推出了 LangServe,让开发者可以一键将应用发布为 REST API。
LangGraph 的崛起与未来:
LangGraph 被视为构建下一代复杂智能代理的关键框架。其发展重点在于:
成为代理架构的首选: 官方明确表示,LangGraph 将是未来构建代理架构(Agentic Architectures)的重点发展方向。
增强可控性和可靠性: LangGraph 的图形化结构和状态管理机制,为设计能够处理复杂任务且行为可预测的代理提供了坚实的基础。
人机协作的无缝整合: 其内置的状态持久化和流程控制能力,使得在代理的执行过程中无缝地加入人类的审核和指导成为可能。
可视化与开发工具: 配合 LangGraph Studio 等可视化开发工具的推出,开发者可以更直观地设计、调试和迭代复杂的代理流程。
在实践中,使用 LangChain 来构建一个基于公司内部文档的问答机器人。整个流程非常清晰:
1 | # 伪代码和步骤解释 (面试时口述) |
“通过这套流程,我能快速搭建一个功能强大的 RAG 系统,整个逻辑是线性和确定的。”
构建一个更智能的研究代理,它能上网搜索,如果结果不满意,还能决定再次搜索。
1 | # 伪代码和步骤解释 (面试时口述) |
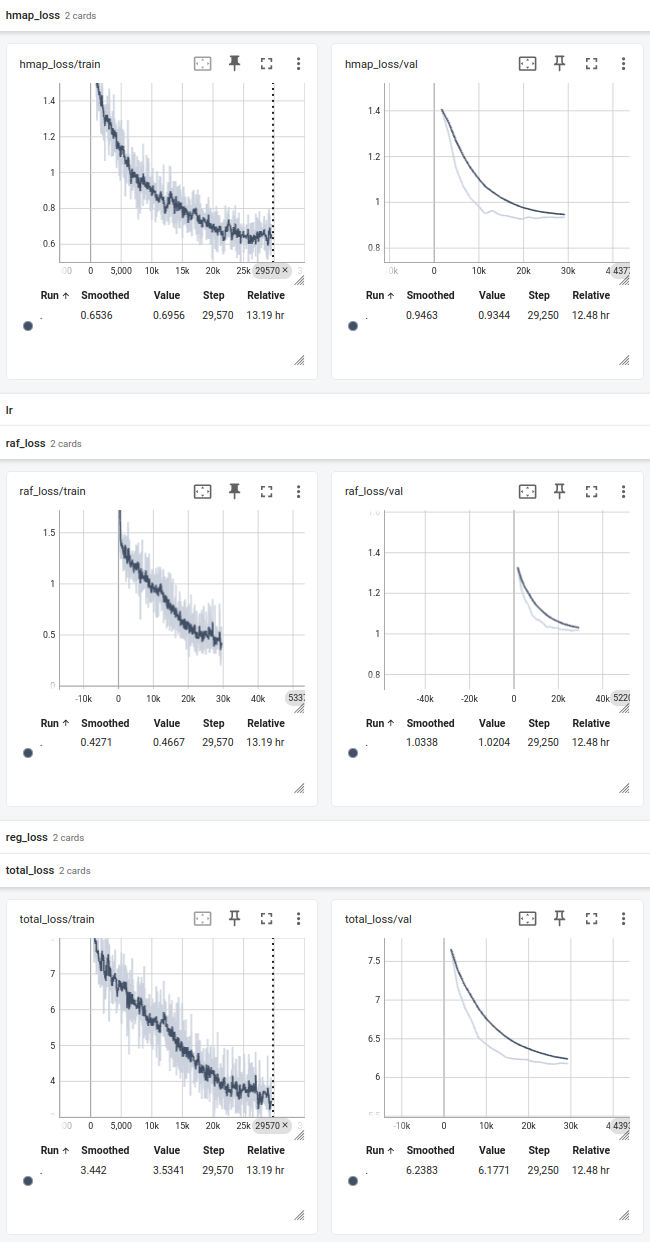
For the figure, the each step corresponds to a processed batch(16).
Course: VV570/MATH6003J: Introduction to Engineering Numerical Analysis 1
1. Introduction & Problem Statement
In robotic perception, sensors like LiDAR capture the environment as a “point cloud”—a set of data points in space. To enable tasks like mapping or localization, a robot must align multiple point clouds taken from different positions. This project will address this fundamental robotics problem by implementing the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm, a numerical optimization method used to find the optimal alignment between two point clouds2.
2. Objective
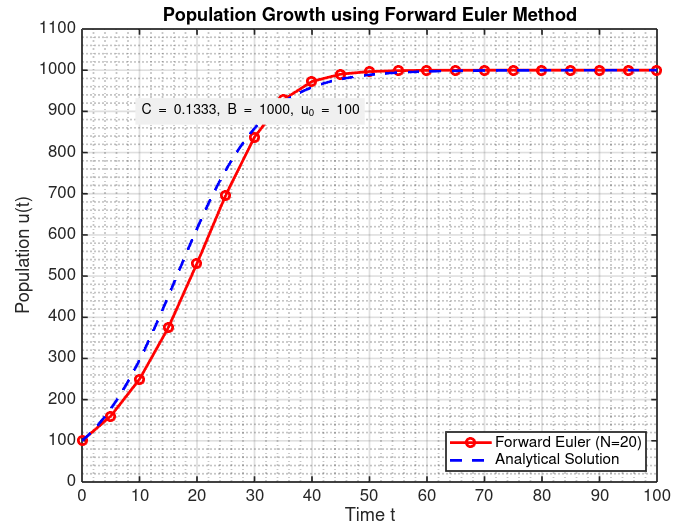
The primary objective of this project is to develop a working 2D implementation of the ICP algorithm. We will apply numerical analysis techniques to find the rigid transformation (rotation and translation) that minimizes the distance between two point clouds, demonstrating a practical application of concepts from the course to the field of robotics.
3. Methodology
Our approach will be to apply a computational tool to solve this problem3. We will use Python with the NumPy library for numerical computations and Matplotlib for visualization. The core steps of our implementation will be:
Data Association: For each point in a source cloud, find the closest corresponding point in the target cloud.
Numerical Optimization: Calculate the optimal rotation and translation that minimizes the mean squared error between the corresponding point pairs. This will be solved using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD).
Iterative Refinement: Apply the calculated transformation to the source cloud and repeat the process until the alignment error converges below a set threshold.
We will start with the simplification of working in 2D and assume a reasonable initial alignment between the point clouds4.
4. Expected Outcomes & Justification of Results
By the end of this three-week project5, we will deliver:
A Python implementation of the 2D ICP algorithm.
Visualizations demonstrating the algorithm’s effectiveness by showing the point clouds before and after alignment.
A plot of the alignment error over iterations, which will serve to justify our results by showing the convergence of the numerical method6.
Zhichen Tang
124370910020
Use SSH to Connect TensorboardX
使用ssh作为命令行远程工具,启动远程的tensorboardx并且在本地的浏览器中打开。
远程运行:
1 | tensorboard --logdir <path> --port 6006 |
本地运行:
1 | ssh -N -f -L localhost:16006:localhost:6006 bohan@10.11.16.146 |