Large-scale visual relationship understanding
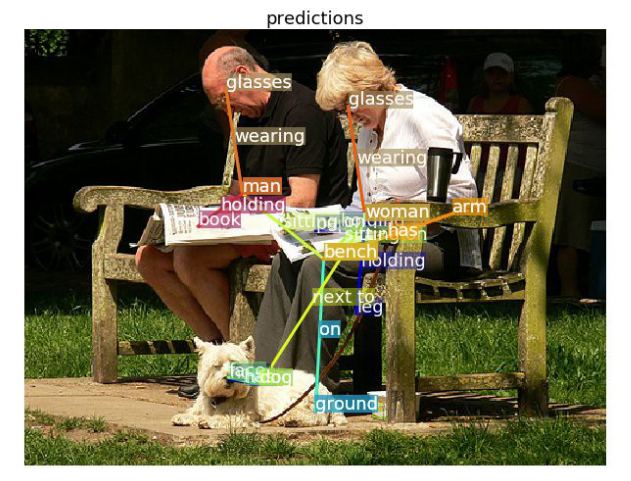
Scene Graph Generation- A comprehensive survey
See [[Reconstruct-Anything Literature Review]]
SceneGraphFusion- Incremental 3D Scene Graph Predictionfrom RGB-D Sequences
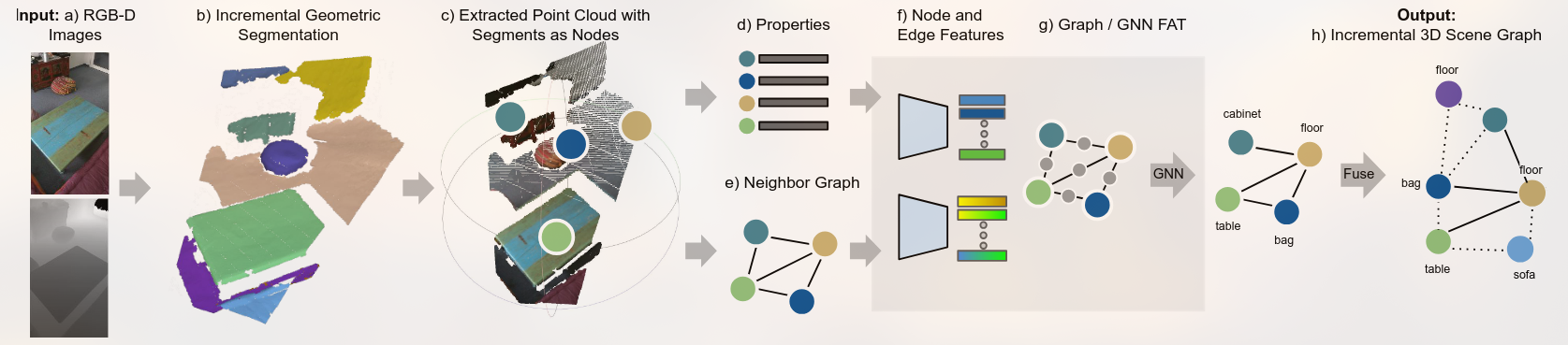
Overview of the proposed SceneGraphFusion framework. Our method takes a stream of RGB-D images a) as input to create an incremental geometric segmentation b). Then, the properties of each segment and a neighbor graph between segments are constructed. The properties d) and neighbor graph e) of the segments that have been updated in the current frame c) are used as the inputs to compute node and edge features f) and to predict a 3D scene graph g). Finally, the predictions are h) fused back into a globally consistent 3D graph.
Scene Reconstruction with Functional Objects for Robot Autonomy
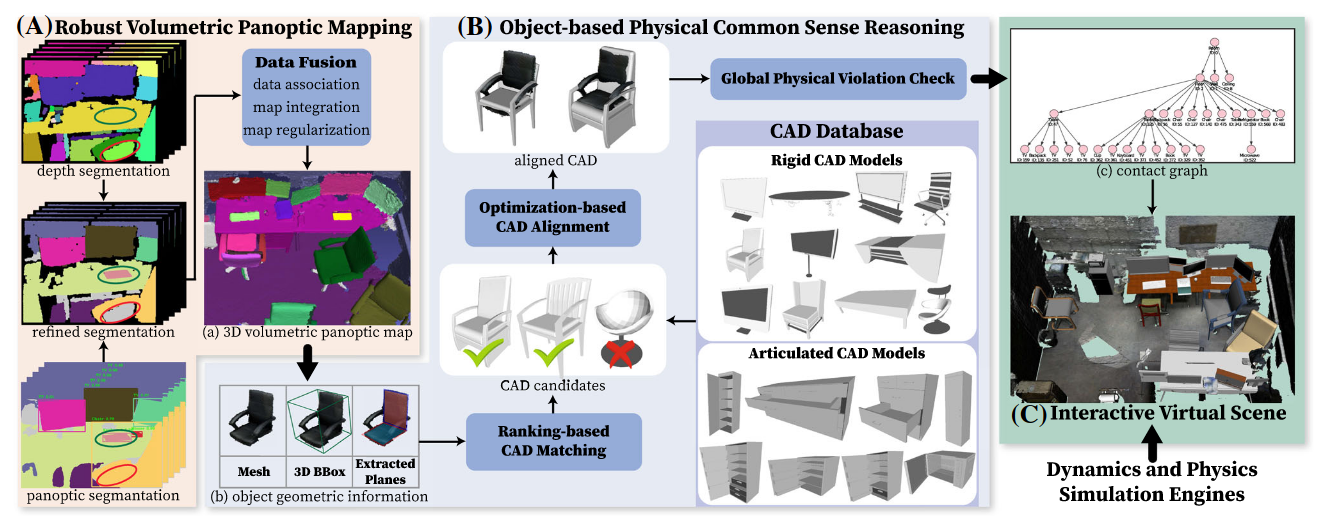
和李飞飞[[ACDC- Automated Creation of Digital Cousins for Robust Policy Learning]]的思想类似。