(Roadmap) Deeper Scene Graph For Robots
 Deeper Scene Graph For Robots/Pasted_image_20250328103811.png)
Robotic planning and execution in open-world environments is a complex problem due to the vast state spaces and high variability of task embodiment.
例如针对家用场景:
(Roadmap) Deeper Scene Graph For Robots
 Deeper Scene Graph For Robots/Pasted_image_20250328103811.png)
Robotic planning and execution in open-world environments is a complex problem due to the vast state spaces and high variability of task embodiment.
例如针对家用场景:
Semantic-SAM Repository Application

My repository: https://github.com/Chen-Yulin/Semantic-SAM
My venv: ssam
Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding
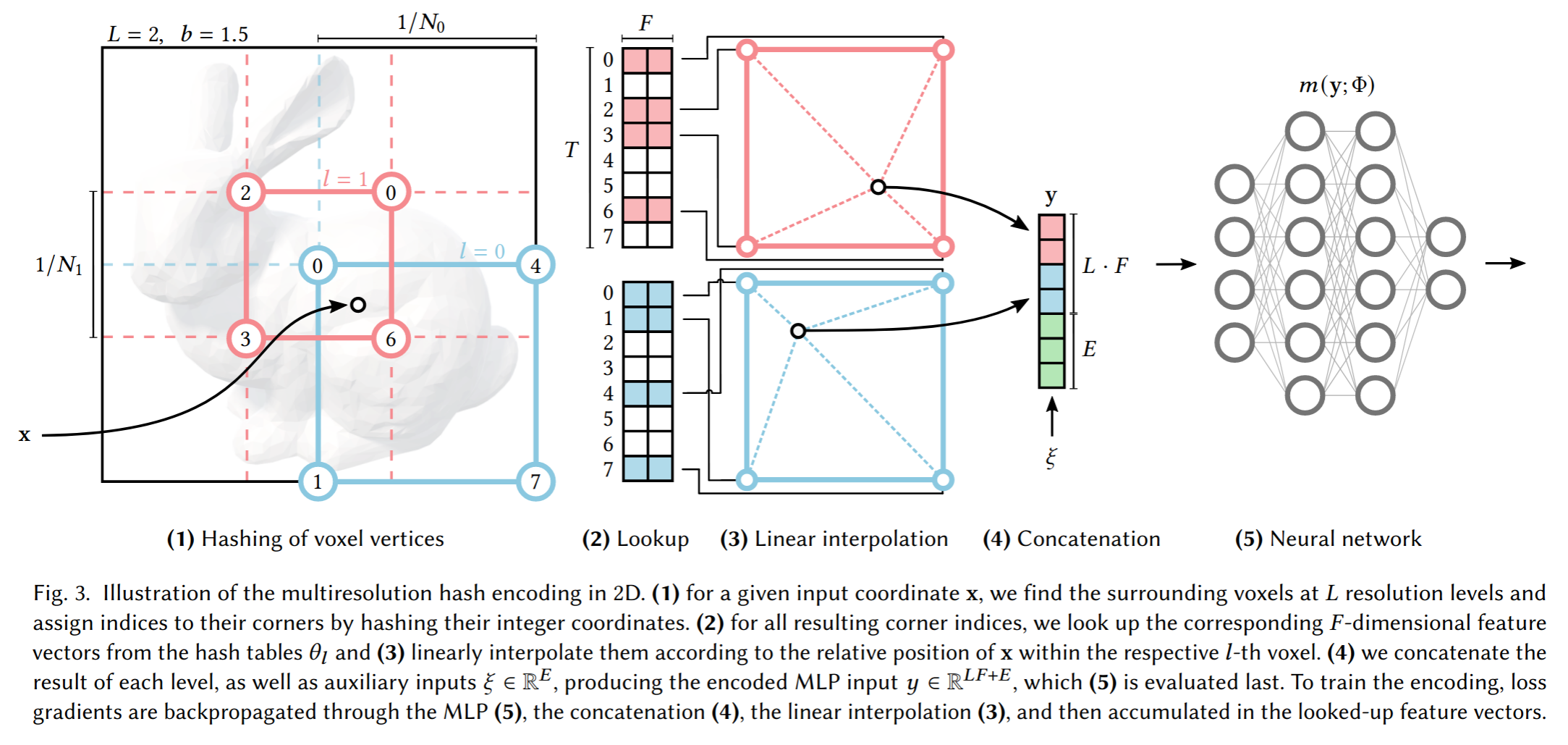
很重要的编码优化论文,MHE的概念:
ConceptGraphs= Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Graphs for Perception and Planning
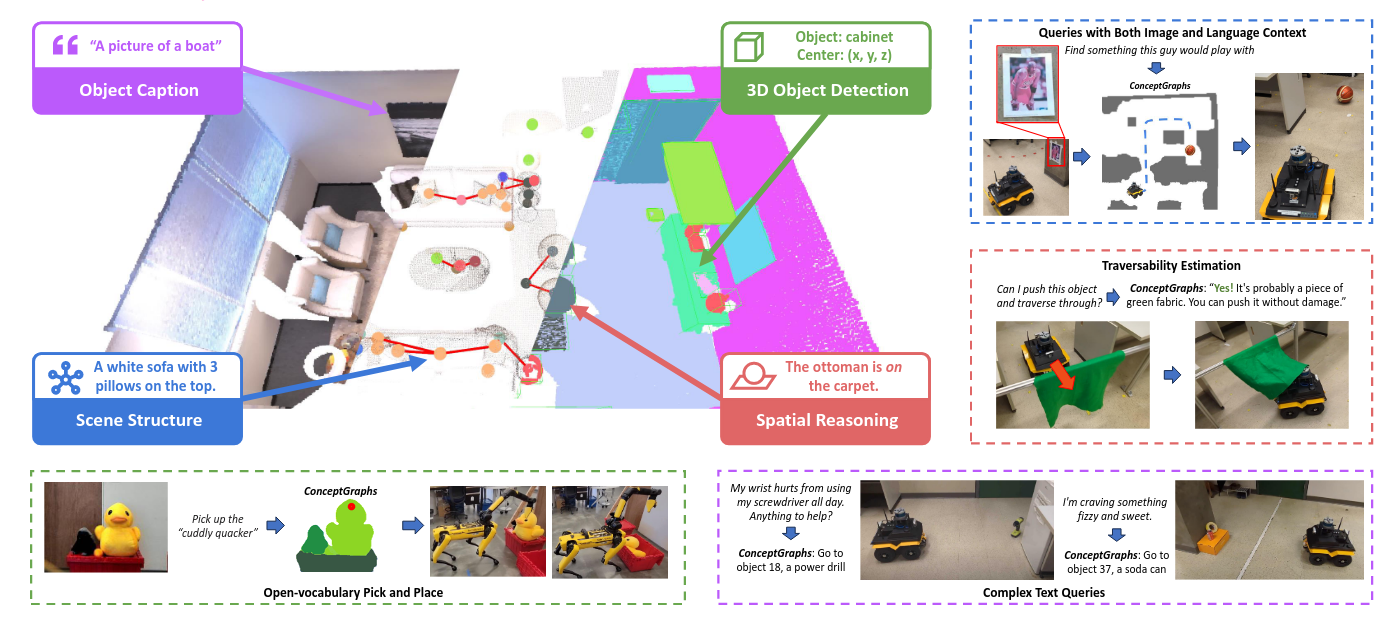
通过LLM来判断位置关系,以此构建scene graph
SayPlan= Grounding Large Language Models using 3D Scene Graphs for Scalable Robot Task Planning
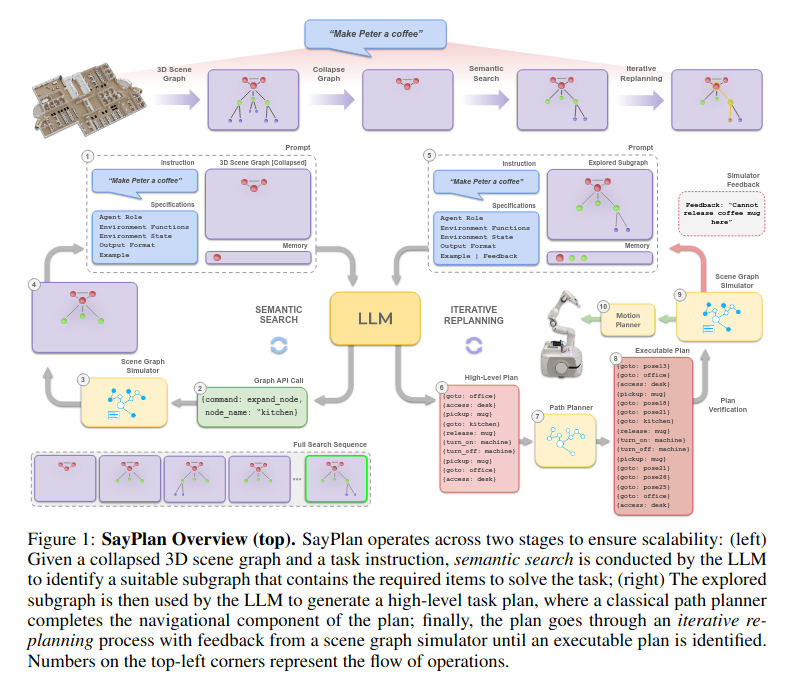
主要的思想都在上面这个伪代码里,通过只展开部分场景图(严格层级结构),来控制输入llm的场景图大小。
Representation Learning for Scene Graph Completion via Jointly Structural and Visual Embedding
 Representation Learning for Scene Graph Completion via Jointly Structural and Visual Embedding/Pasted_image_20250318162533.png)
The architecture of RLSV is a three-layered hierarchical projection that projects a visual triple onto the attribute space, the relation space, and the visual space in order.