Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding
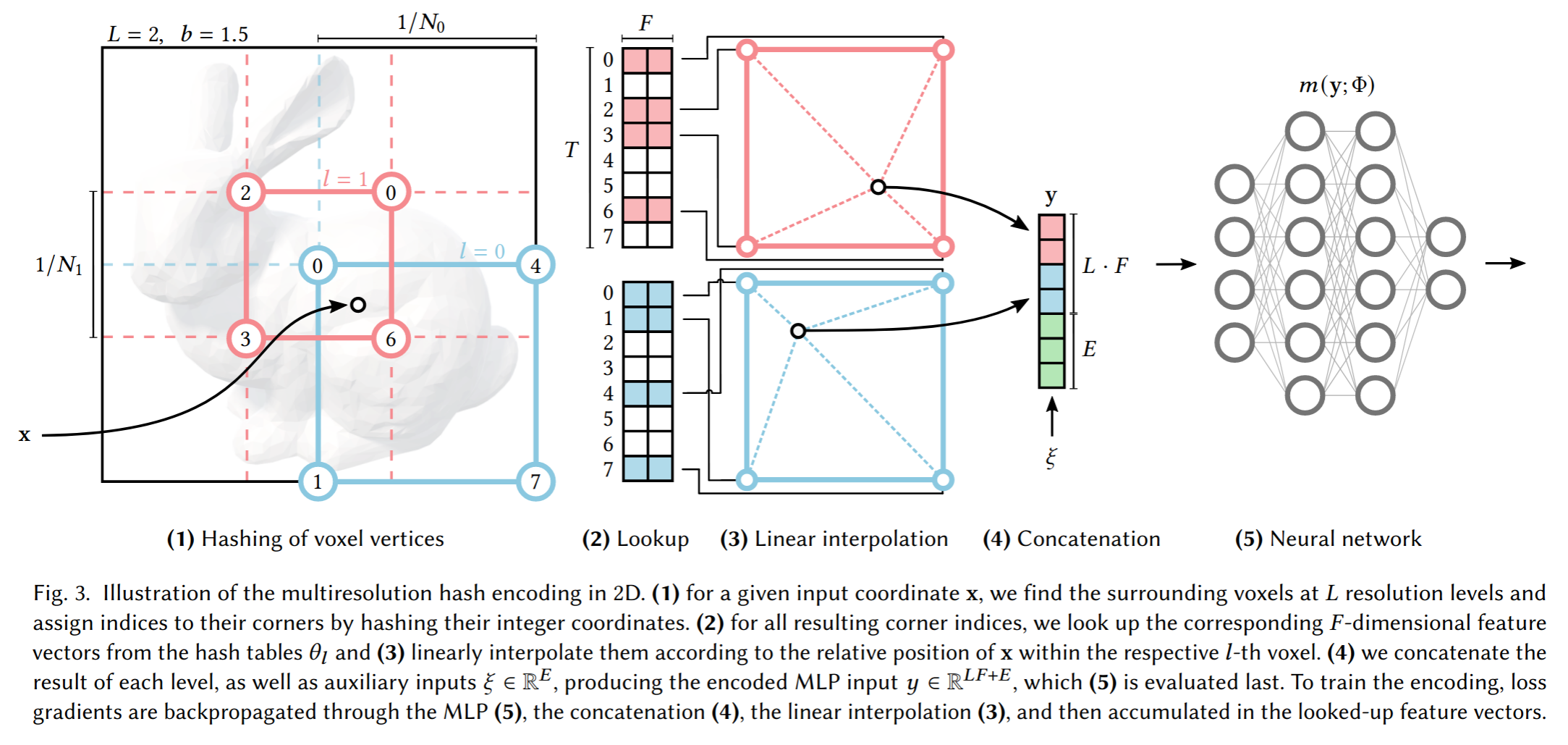
很重要的编码优化论文,MHE的概念:
Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding

很重要的编码优化论文,MHE的概念:
SceneGraphFusion- Incremental 3D Scene Graph Predictionfrom RGB-D Sequences
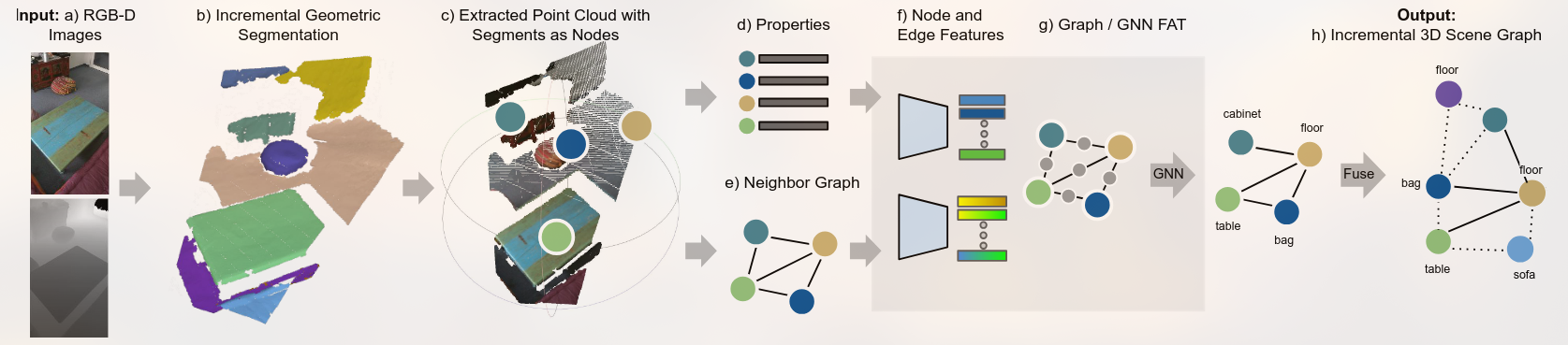
Overview of the proposed SceneGraphFusion framework. Our method takes a stream of RGB-D images a) as input to create an incremental geometric segmentation b). Then, the properties of each segment and a neighbor graph between segments are constructed. The properties d) and neighbor graph e) of the segments that have been updated in the current frame c) are used as the inputs to compute node and edge features f) and to predict a 3D scene graph g). Finally, the predictions are h) fused back into a globally consistent 3D graph.
Scene Reconstruction with Functional Objects for Robot Autonomy
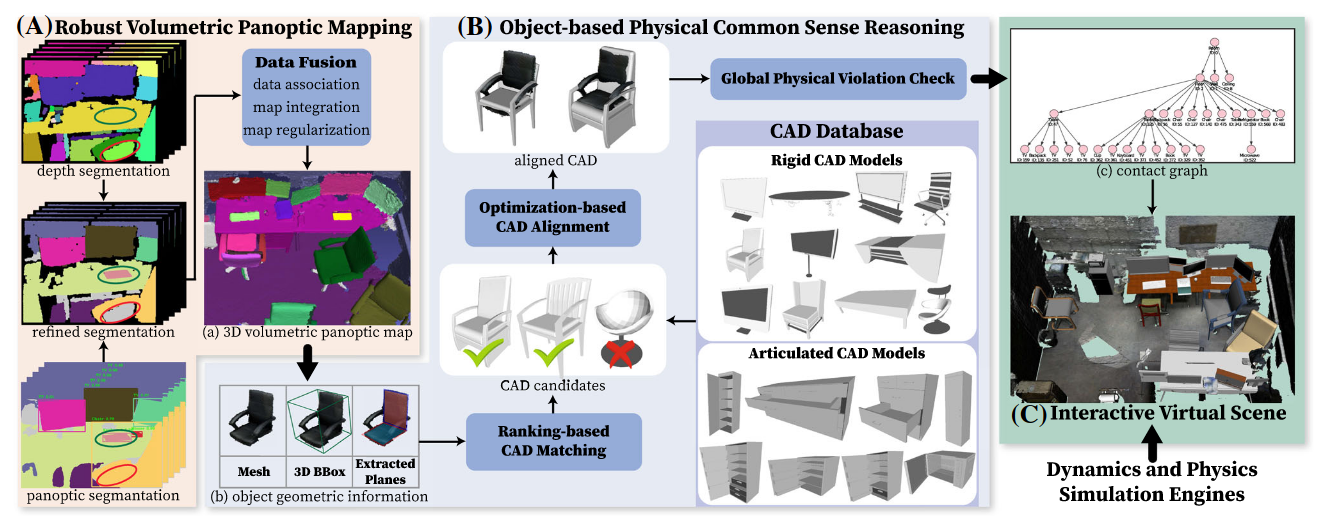
和李飞飞[[ACDC- Automated Creation of Digital Cousins for Robust Policy Learning]]的思想类似。
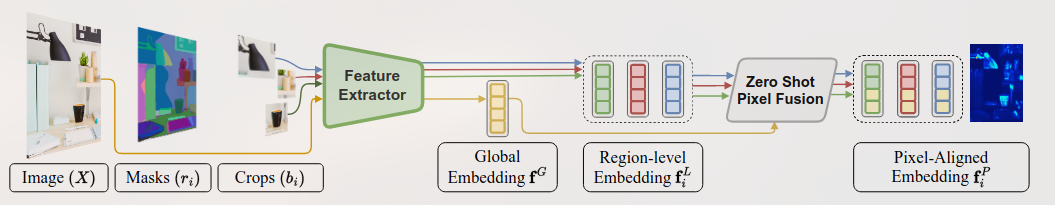
将不同帧$X_t$中的特征集合在M中特征点的公式:
Some Thoughts Regarding -Reconstruct Anything-
主要记录一些读场景语义化重建的论文的过程中的想法
限定:暂不考虑机器人的移动性,也就是不需要跨视野的导航(OK-Robot),暂定为桌面机器人
具体来说,通用机器人的特点包括:
受DINO自蒸馏自监督的启发,可以通过物体活动的图像序列来推测物体各个部分的物理关系(attention map)[[DINO]]
训练集可以使用Unity生成不同的光影/物体,连接语义
voxel collider for detected objects, joints, physics agent interact with physics engine.
点云数据,grounded caption=>object property, hierarchy relation, joints(maybe new model should be proposed)
受[[BLIP]]启发,understanding for language & existing point cloud, generation for the rest of the point cloud (Wonder3D已实现)
OK-Robot- What Really Matters in Integrating Open-Knowledge Models for Robotics

Creating a general-purpose robot has been a longstanding dream of the robotics community.