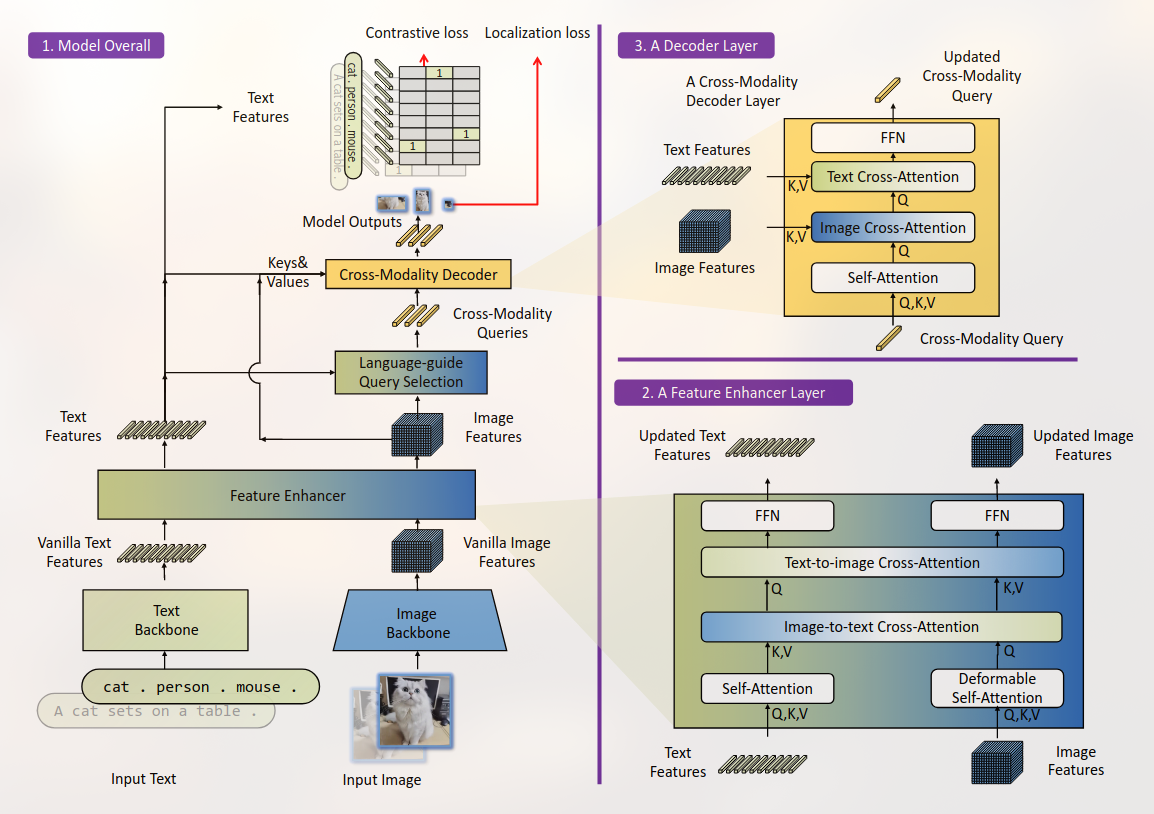

A vision-language model that unifies vision-language understanding and generation tasks.

A vision-language model that unifies vision-language understanding and generation tasks.
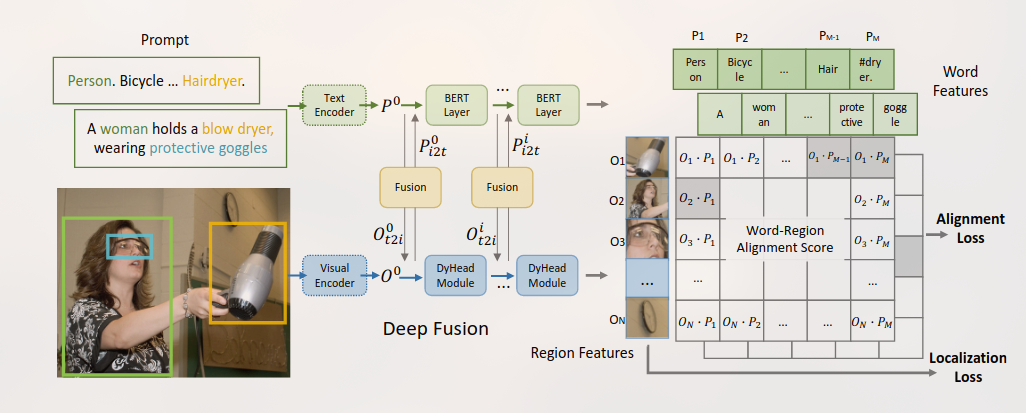
GLIP是一个学习了object-level, language-aware, and semantic-rich visual representations 的模型。
统一对象检测和短语接地进行预训练。
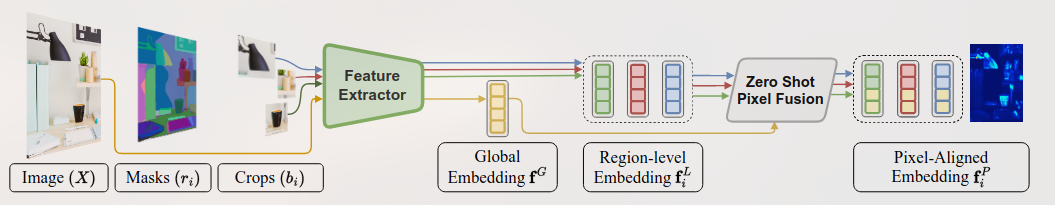
将不同帧$X_t$中的特征集合在M中特征点的公式:
https://github.com/IDEA-Research/Grounded-Segment-Anything
By [[Grounding-DINO]] + SAM
Achieving Open-Vocab. Det & Seg
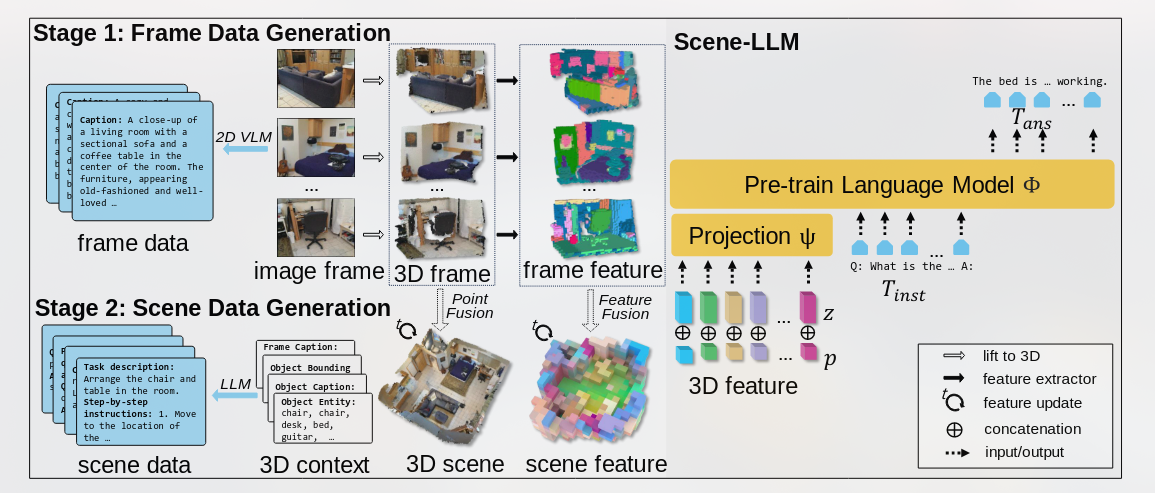
本文提出的模型主要想解决3D密集标注和交互式规划。
结合
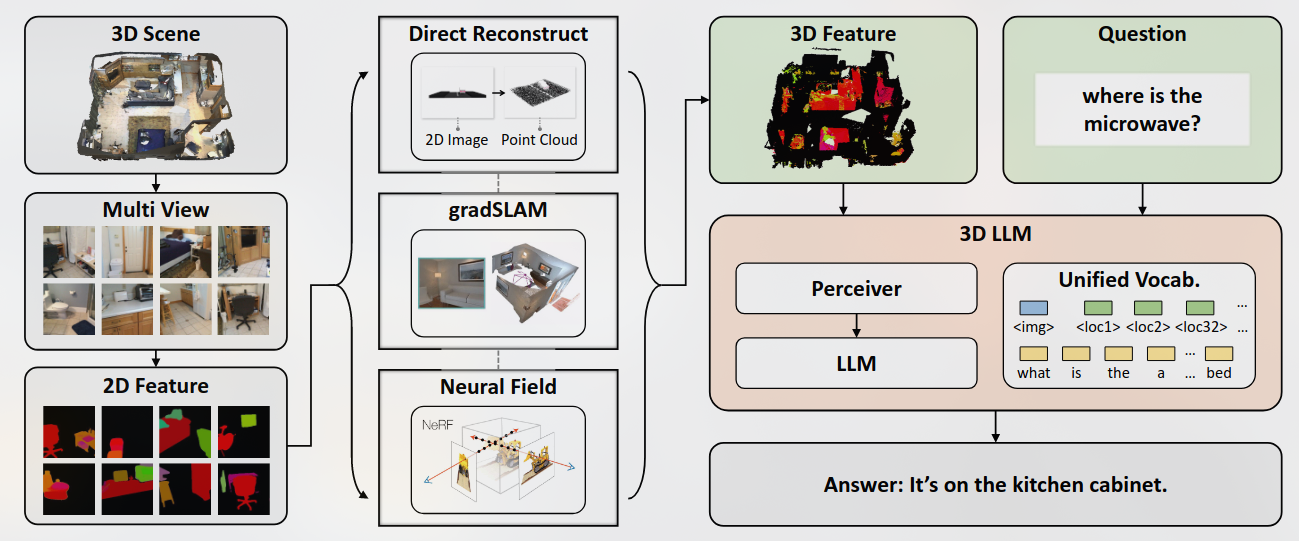
Recent works have explored aligning images and videos with LLM for a new generation of multi-modal LLMs that equip LLMs with the ability to understand and reason about 2D images.
但是仍缺少对于3D物理空间进行分析的模型, which involves richer concepts such as spatial relationships, affordances, physics and interaction so on.