LingBot-VLA: A Pragmatic VLA Foundation Model
论文链接 | GitHub | Checkpoints
研究背景
视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)基础模型是机器人操作领域的新兴方法,通过大规模预训练使机器人能够执行由自然语言指令引导的多样化操作任务。然而,目前存在以下问题:
- 缺乏关于真实机器人性能如何随预训练数据规模增长而变化的系统性实证研究
- 缺乏高效的训练代码库来支持大规模数据的扩展评估
- 缺乏跨多平台、多任务的系统性真实世界评估基准
研究目标
- 探索 VLA 模型在真实世界机器人数据上的扩展规律(Scaling Law)
- 建立跨多平台、多任务的系统性真实世界评估基准
- 开发高效的大规模 VLA 训练代码库
核心概念
Mixture-of-Transformers (MoT) 架构
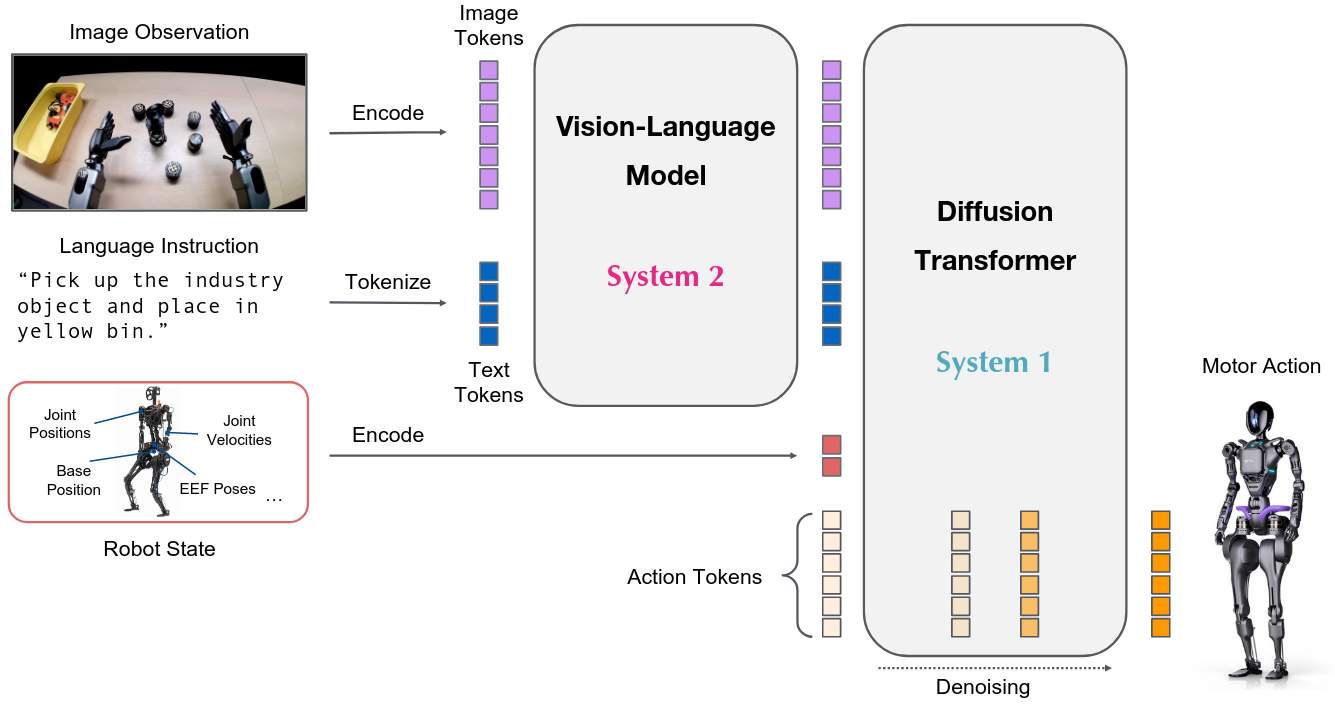
将预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)与动作生成模块(Action Expert)结合,通过共享自注意力机制实现跨模态统一建模。视觉-语言和动作模态通过独立的 Transformer 路径处理,既保留 VLM 的语义先验,又避免跨模态干扰。
Flow Matching
一种用于连续动作建模的生成方法,通过学习从噪声到目标动作的向量场来生成平滑的机器人控制信号。
Blockwise Causal Attention
将序列划分为图像-指令块、状态块和动作块,应用因果掩码防止信息泄露,确保动作预测只能访问当前和历史观测信息。
研究方法
模型架构
LingBot-VLA 采用 MoT 架构,整合 Qwen2.5-VL 作为视觉语言骨干网络,配合独立的 Action Expert 模块:
联合建模序列:
$$[O_t, A_t] = [I_t^1, I_t^2, I_t^3, T_t, s_t, a_t, a_{t+1}, \ldots, a_{t+T-1}]$$
其中 $I_t^{1,2,3}$ 为三视角图像,$T_t$ 为任务指令,$s_t$ 为机器人状态,$A_t$ 为动作序列(chunk length = 50)。
类似[[BAGEL-Unified-Multimodal-Pretraining]]
Flow Matching 目标函数
定义概率路径通过线性插值:
$$A_{t,s} = sA_t + (1-s)\epsilon, \quad \epsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I)$$
训练目标:
$$\mathcal{L}{FM} = \mathbb{E}{s \sim U[0,1], A_t, \epsilon}|v_\theta(A_{t,s}, O_t, s) - (A_t - \epsilon)|^2$$
深度信息蒸馏
通过可学习查询 $Q_t$ 与 LingBot-Depth 模型的深度 token $D_t$ 对齐,增强空间感知:
$$\mathcal{L}{distill} = \mathbb{E}{Q_t}|Proj(Q_t) - D_t|$$
训练效率优化
- FSDP 分布式策略:采用混合分片数据并行(HSDP),为 Action Expert 模块构建专用分片组
- 算子级优化:使用 FlexAttention 优化稀疏注意力计算,torch.compile 进行算子融合
- 混合精度:reduction 使用 float32,存储和通信使用 bfloat16
主要发现
扩展规律验证
- 预训练数据从 3,000 小时扩展到 20,000 小时,下游任务成功率持续显著提升
- 在 20,000 小时数据量下仍未出现饱和迹象,表明 VLA 性能持续受益于数据量增加
- 首次提供了真实世界机器人学习中有利扩展特性的实证证据
数据效率
- 仅使用 80 个演示即可超越 π0.5 使用 130 个演示的性能
- 随着后训练数据量增加,与基线的性能差距进一步扩大
实验设计
预训练数据
- 规模:约 20,000 小时真实世界操作数据
- 来源:9 种双臂机器人平台(AgiBot G1、AgileX、Galaxea R1Lite/R1Pro、Realman Rs-02、Leju KUAVO、Qinglong、ARX Lift2、Bimanual Franka)
评估基准
- GM-100 基准:100 个操作任务,39,000 个专家演示
- 评估规模:3 个机器人平台,每任务 130 个后训练 episode,共 22,500 次试验
- 对比方法:π0.5、GR00T N1.6、WALL-OSS
真实世界评估结果
| 方法 | 平均成功率(SR) | 平均进度分(PS) |
|---|---|---|
| WALL-OSS | 4.05% | 10.35% |
| GR00T N1.6 | 7.59% | 15.99% |
| π0.5 | 13.02% | 27.65% |
| LingBot-VLA w/o depth | 15.74% | 33.69% |
| LingBot-VLA w/ depth | 17.30% | 35.41% |
仿真评估结果(RoboTwin 2.0)
| 方法 | Clean 场景 SR | Randomized 场景 SR |
|---|---|---|
| π0.5 | 82.74% | 76.76% |
| LingBot-VLA w/o depth | 86.50% | 85.34% |
| LingBot-VLA w/ depth | 88.56% | 86.68% |
训练吞吐量
- 实现 261 samples/s/GPU(8-GPU 配置)
- 相比 StarVLA、DexBotic、OpenPI 提升 1.5~2.8 倍
- 在 256 GPU 规模下仍保持接近线性扩展
讨论
优势
- 首次在大规模真实世界数据上验证 VLA 扩展规律
- 显著优于现有 SOTA 方法的多平台泛化能力
- 高效的训练代码库,支持大规模分布式训练
- 开源代码、模型和基准数据
局限性
- 目前仅支持双臂机器人配置
- 评估主要集中在桌面操作任务
- 深度信息蒸馏依赖额外的 LingBot-Depth 模型
相关工作
Foundation VLA
- π0:Vision-language-action flow model for general robot control
- π0.5:VLA model with open-world generalization
- GR00T N1.6:Open foundation model for generalist humanoid robots
Spatial VLA
- SpatialVLA:探索 VLA 模型的空间表示
- Spatial Forcing:通过对齐策略增强 VLA 空间理解
- GeoVLA:赋能 VLA 模型 3D 表示能力
高效训练框架
- OpenPI:支持 JAX 和 PyTorch 的 π 系列模型训练框架
- StarVLA:VLA 和 VLM 联合训练的模块化代码库
- DexBotic:统一高效��� VLA 开发生命周期解决方案
未来方向
- 扩展机器人类型:整合单臂和移动机器人数据,支持更多样化的操作能力
- 非约束环境:探索在非结构化环境中的移动操作能力
- 持续扩展:进一步扩大预训练数据规模,探索扩展规律的上限
参考文献
- Black et al. (2025). π0: A vision-language-action flow model for general robot control. RSS.
- Black et al. (2025). π0.5: A vision-language-action model with open-world generalization. CoRL.
- Bjorck et al. (2025). GR00T N1: An open foundation model for generalist humanoid robots. arXiv.
- Bai et al. (2025). Qwen2.5-VL technical report. arXiv.
- Lipman et al. (2022). Flow matching for generative modeling. arXiv.
- Wang et al. (2026). The Great March 100: 100 detail-oriented tasks for evaluating embodied AI agents.