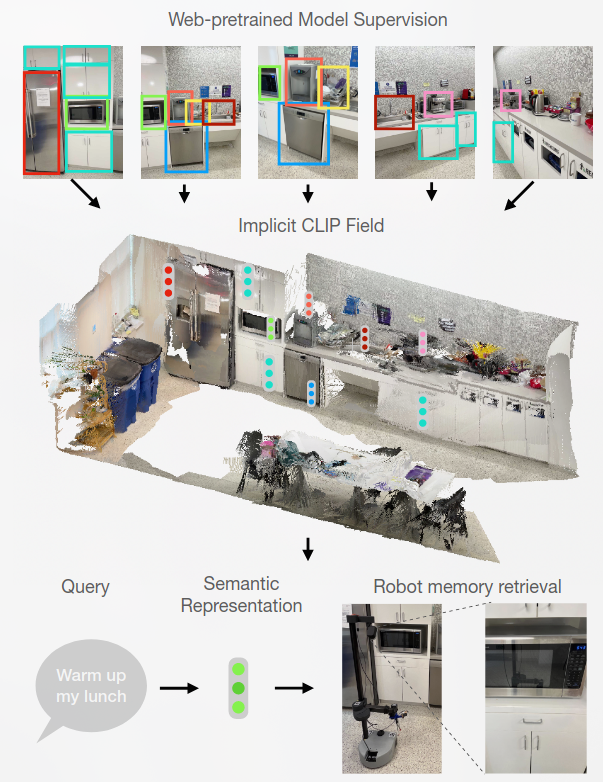
LERF- Language Embedded Radiance Fields

NeRF+CLIP
OK-Robot- What Really Matters in Integrating Open-Knowledge Models for Robotics

Creating a general-purpose robot has been a longstanding dream of the robotics community.
Dynamic Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Graphs for Long-term Language-Guided Mobile Manipulation
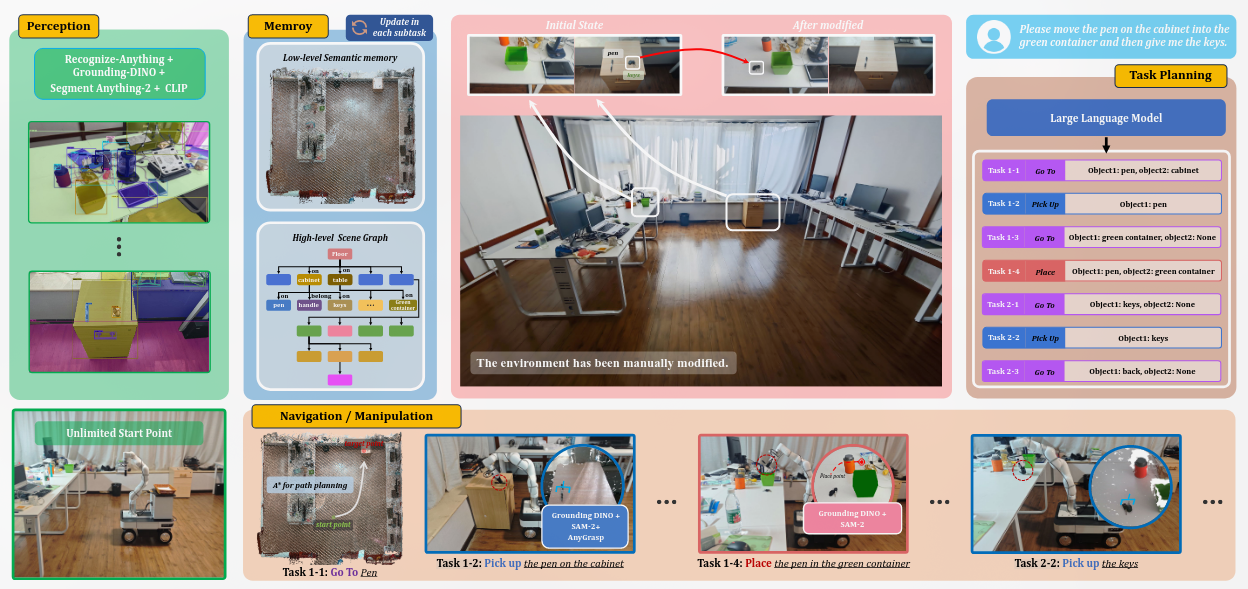
和我的想法非常相近,完成度也很高啊喂。可以参考他的实现思路,引用的文章等等。